Each market only offers so much room for growth. Successful business owners eventually consider expanding their operations to continue growing and reaching more customers.
Generating more sales or capturing a larger share of the market requires a business expansion strategy. Common expansion strategies include adding new locations, developing new products, and partnering or merging with other companies. The strategy used is often influenced by the industry and target audience.
Breaking into a new market or expanding your offerings involves a lot of work. Before you can go to market with a new product or marketing campaign, you need a plan.
Use the following guide to develop an expansion strategy for increasing your odds of success. You will find strategies for expanding your business on a low budget, expanding startups, and other solutions for growing your business. here you can find the ultimate business expansion guide
Organic vs Non-Organic Growth Strategies
Business expansion is the process of increasing your market share, customer base, or revenue. You may achieve these goals using a broad range of growth strategies. However, most expansion strategies are classified as organic or non-organic.
Organic growth comes from expanding your business’s output or efficiency. You may develop new products, enter new markets, or increase the productivity of your current business processes.
Non-organic growth comes from external activities. Mergers, acquisitions, and partnerships are all examples of external expansion.
Advantages of Organic Growth
Organic growth comes from your established business practices. You may increase sales of current products, create new products, or enter new markets.
Despite the name, organic growth does not come automatically. You still need to plan and strategize. Here are a few of the reasons to consider using an organic growth strategy:
- Limited restructuring
- Retain more control
- Increased sustainability
- Lower upfront costs
Organic growth often involves less internal restructuring compared to inorganic/nonorganic strategies. Instead of merging or partnering with another company, you expand existing practices or add new ones.
Organic growth requires you to remain committed to your core business. You find ways to improve and expand without input from partners or acquired companies. This gives you more control over your business decisions.
Organic growth is also essential for sustainability. You need to continue growing organically if you expect to continue acquiring customers. Each market has a limit on available customers. A smaller market may not support long-term growth, which is why many businesses eventually expand to other markets.
Compared to a partnership or an acquisition, organic growth strategies may result in lower upfront costs. Most organic expansion methods involve smaller transactions that require less capital compared to an acquisition.

Advantages of Non-Organic Growth
Nonorganic growth involves leveraging external resources to expand your market share or revenue. These resources are from other companies. Most external growth strategies revolve around mergers, acquisitions, and partnerships.
A merger is a strategy that occurs through a takeover or an amalgamation. A takeover/acquisition involves buying a majority stake in another organization. After purchasing the company, you assume control over its operations.
Amalgamation is the process of merging two or more organizations to form a new entity. Acquisitions and amalgamations offer increased economies of scale. You can instantly expand your reach and enjoy the following benefits:
- Faster progress
- Increased market share
- Competitive advantage
- Knowledge and experience
Merging with another company can lead to faster progress on your expansion plans. Organic growth often involves gradually getting your foot in the door of a new market. Inorganic growth allows you to quickly benefit from external resources from another company.
You may also quickly increase your market share. Leveraging another company’s existing customer base gives you a larger share of the market with less effort compared to organic/internal expansion.
Increasing your market share through a merger also provides a competitive advantage. The combined customer base of the companies involved in the merger may exceed the market share of leading competitors.
Access to knowledge and experience is an often-overlooked advantage of mergers. After the merger, key executives from the other companies may remain with the organization, offering access to their expertise.
Keep in mind that external growth can also come with drawbacks. Depending on the terms of the arrangement, mergers can limit control of the direction of the business. You may also need to come up with increased capital and spend more time restructuring to accommodate the combined operations.

Is a Joint Venture an Internal or External Growth Strategy?
A joint venture is a form of external growth. It involves working with one or more partners to establish new business operations. Joint ventures may also involve combining forces to secure a larger share of the market. While a joint venture is an external growth strategy, it allows you to avoid some of the risks of an acquisition or an amalgamation.
For example, the initial costs are often lower compared to an acquisition. You also retain control of your core business. However, you still may share decision-making processes involving the joint venture.
Whether to focus on internal or external expansion depends on your current situation. Partnering or merging with another company may not solve internal problems. If you currently face declining growth, you may benefit from fixing internal processes before seeking external growth.
On the other side of the spectrum, businesses experiencing slow, steady growth may seek external expansion opportunities to build on their current level of success.

10 Types of Expansion Strategies
You have a variety of strategies available for achieving internal or external expansion. Here are 10 of the most common business expansion strategies:
- Market penetration
- Market expansion
- Geographical expansion
- Diversification
- Vertical integration
- New distribution channels
- Product development
- Investments
- Share of wallet (SOW) growth
- Market segmentation
Each of these strategies involves separate steps, risks, and opportunities. Explore the details of each strategy while considering whether it aligns with your business goals.
1. Market Penetration
Market penetration is your share of the market that you are currently competing in. You can achieve greater penetration through organic or inorganic growth strategies.
For example, developing products and increasing productivity are internal strategies. Mergers are external strategies. All three methods can help you acquire more customers in your current market.
Common market penetration strategies include:
- Adjusting prices
- Improving products
- Using more distribution channels
- Increasing marketing efforts
Adjusting prices is a common method for achieving greater market penetration. Lowering your prices may make your products more accessible to a larger portion of your chosen market. However, lowering prices can also limit revenue if you fail to acquire new customers.
You may also focus on improving your products or services. Making improvements may result in greater customer retention in addition to capturing a larger share of the market.
Increasing the quality of your offerings also offers long-term advantages. It gives you a solid base for building greater customer loyalty and retention.
Adding more distribution channels is another way to reach more customers in your current market. If you currently rely only on online sales, finding local retail outlets or distributors may allow more customers to find your products or service.
Along with using more distribution channels, you may try using more marketing channels. For example, you can take advantage of offline marketing channels, such as television, radio, and print media. Flyer and leaflet distribution are also effective offline marketing solutions.
In our guide to adapting your marketing strategy for the new normal after the emergence of COVID, we revealed that one client achieved a 30% conversion rate with their leaflet distribution campaign.
Using more distribution channels and marketing strategies can help you connect with a larger segment of your market. You may be able to attract more attention to your products or services to achieve deeper market penetration.
Pros
- Often requires fewer resources
- May help you surpass the competition
Cons
- Adjusting your prices can create extra risks
- Limited potential for sustainable growth


2. Market Expansion
As with market penetration, the market expansion strategy is focused on your current market. However, instead of capturing a larger share of your existing target audience, you attempt to expand your customer base.
For example, a business may increase its selection of products to reach an untapped segment of the market. A software development company may focus on different industries. A local restaurant may add menu items that appeal to different demographics.
You can use existing or new products or services as part of your market expansion efforts. If you plan on using existing products, expanding your market campaigns can help you reach a larger audience.
If you intend to develop a new product, focus heavily on the needs of the audience that you want to tap into. Perform thorough consumer research to identify their pain points to ensure that your new product addresses their needs.
Mergers also provide a solution for market expansion. Merging with a company in the same industry with a different share of the market instantly increases your customer base.
One of the challenges of market expansion is scaling your operations. You need to plan for increased output to avoid spreading your resources too thin.
Pros
- You can reach a larger audience
- You may not need to switch industries or markets
Cons
- You risk spreading existing resources thin
- Smaller markets have limited room for expansion

3. Geographical Expansion
Geographical expansion is a form of expansion that involves entering new markets in different regions. You may expand the scope of your marketing to target customers in other cities, states, or countries. However, a geographical expansion strategy also typically involves sticking with the same industry.
For example, you may open new locations in another city or state to serve a larger customer base. Increasing your output and selling through distributors in another region is also an example of geographical expansion.
Entering new markets offers many advantages, including the opportunity for consistent, sustainable growth. When you enter a new market, you have an entirely new group of customers to target. You can also continue to focus on your existing industry instead of increasing the scope of your operations.
The geographical expansion strategy also comes with challenges, including the logistics of distributing your products or services in new regions. You may need to open new offices, hire more employees, or localize your products to comply with different regulations and standards.
Pros
- Allows you to reach more markets in the same industry
- Provides the opportunity for sustainable growth
Cons
- Logistical challenges of entering a new market
- Localization may be necessary for some products and services

4. Diversification
Diversification is the process of creating new products for a new market. You may start selling a new product in an international market or attempt to break into a related industry in your local area.
Diversified companies are often involved in multiple industries. Large conglomerates have diversified revenue streams. For example, General Electric produces goods and services in the aviation, energy, weapons, locomotive, and finance industries.
Diversifying your operations can help limit economic risk. Spreading your business across multiple industries and markets helps you weather volatility due to disruptions in specific industries.
Diversification may also be an effective solution for businesses dealing with declining growth. If your core business is in decline, entering a new market or industry may lead to greater revenue and new customer acquisition.
Yet, diversification also requires you to learn new skills and obtain new resources. You may need to develop new products or services or find a partner to help you reach new industries.
Pros
- Diversification helps reduce economic risk
- You can add new markets to your growing customer base
Cons
- Entering a new industry requires more resources
- Your core business may suffer from the increased focus on a new industry
5. Vertical Integration
Vertical integration involves relying less on third parties to carry out your business operations. Companies that explore vertical integration strategies may start handling distribution or packaging internally instead of working with an external partner.
Vertical integration allows you to control more of the processes involved in producing and distributing your products. However, adopting new business processes costs money. You may need to purchase new facilities, train new staff, and learn how to navigate other areas of your industry.
Vertical integration can come with higher upfront costs to get everything up and running. Yet, it can help increase your profit margins in the long run.
Pros
- Vertical integration gives you more control
- You may increase your profit margins
Cons
- May involve high upfront costs

6. New Distribution Channels
Using new distribution channels can help maximize your revenue without developing new products or entering a new market. You simply find new ways to reach customers.
For example, after the rise of the internet, brick-and-mortar stores started selling products online. They took advantage of a new distribution channel to connect with a larger customer base.
Adding more distribution channels is one of the strategies used for increasing market penetration. It may also help you expand your market or enter new ones. Try looking for distributors or partners that operate outside of your existing markets or geographic region.
Using a new distribution channel helps you reach more people but also adds to your costs. You may also need to deal with unforeseen costs when adopting a distribution channel that you have limited experience with.
Pros
- Allows you to reach more customers
- You can distribute to new or existing markets
Cons
- Increased risk of unplanned costs

7. Product Development
Product development is one of the most common business expansion strategies. It is typically a form of internal growth. You develop a product internally and sell it to customers. However, joint ventures and mergers can also involve the development of new goods and services.
Developing new products allows businesses to target new and existing customers. For example, you may buy a new phone or tablet every couple of years. The leading electronics manufacturers release new phones and tablets seemingly every year, creating the need to upgrade to a newer model.
Product development can be time-consuming compared to other business expansion strategies. The typical new product timeline is anywhere from a few weeks to several years, depending on the amount of research & development needed.
Product development also comes with greater risks. For example, you may face delays that push back your expansion plans. According to a Gartner Survey, 45% of product launches are delayed by at least a month.
Pros
- Product development is often a necessary step for continued growth
- Releasing new products helps you retain and acquire customers
Cons
- Developing a product is often a major investment of labor, funds, and time
- Product development projects often face delays

8. Investments
People often think of investing as a method for growing personal wealth. However, businesses can also invest. The largest companies invest a portion of their revenue to continue growing their assets.
Investing may involve purchasing stocks or bonds. Businesses may also directly invest in other companies in exchange for partial ownership.
Investments provide a hedge against the risk of a reduction in sales in your core business. Your investments may continue to grow, no matter the success or failure of your business.
Investing in other companies is also often a starting point for partnerships and mergers. As your investment in a company grows, you gradually increase your share of ownership. Major stakeholders may receive seats on the company’s board. You also reduce the remaining capital needed to complete a merger.
Pros
- Investments hedge against risks in your core business
- Investing in other businesses may lead to merger opportunities
Cons
- All types of investments come with risks that you cannot control

9. Share of Wallet (SOW) Growth
Share of Wallet (SOW) is the amount that the average customer spends on a specific brand instead of the brand’s leading competitors in the same category. Increasing your SOW typically requires internal growth.
For example, increasing the quality of your services or products may lead existing customers to spend more. The goal is to maximize revenue from your existing customers (this will also increase the life time value of a consumer). Common strategies for increasing SOW include introducing more products, improving existing products, or releasing add-ons for existing products.
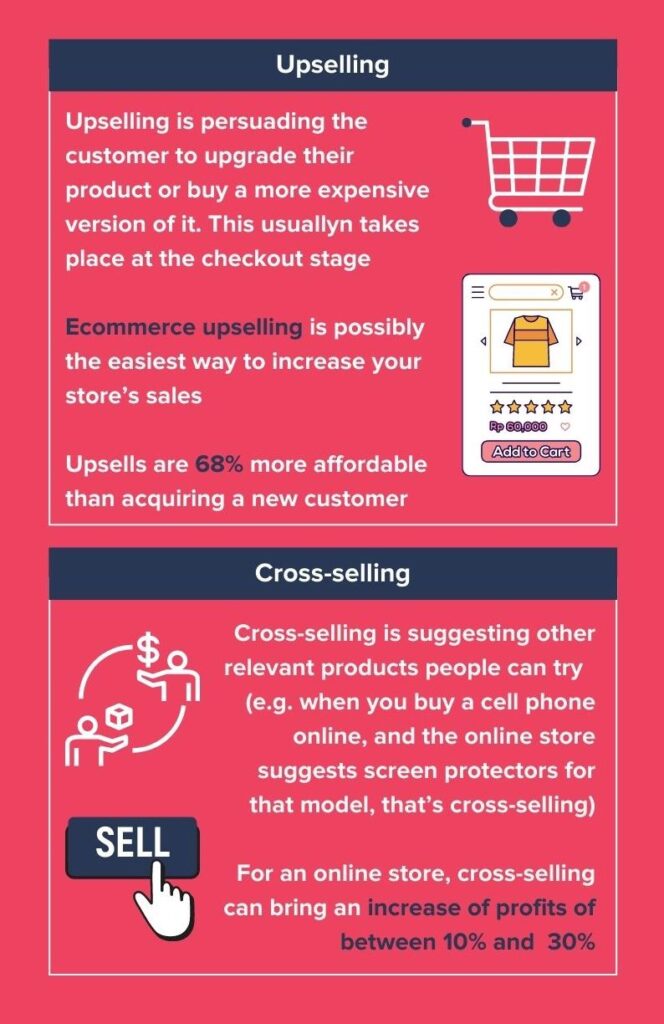
The efforts involved in SOW growth are often less expensive compared to expanding your overall market share. You target existing customers through upselling and cross-selling strategies. Upselling involves promoting a higher-priced product while cross-selling involves promoting related or complementary products.
Pros
- SOW growth helps you increase market penetration
- SOW growth strategies are often cost-effective
Cons
- Smaller markets may offer limited room for revenue growth
10. Market Segmentation
Market segmentation is a form of internal expansion that focuses on a smaller segment of a market. It typically involves zeroing in on a niche segment and building your products or services around their specific needs.
Market segmentation is a common strategy for small businesses looking to compete with larger businesses. By catering to a niche portion of the market, a small business can deliver more personalized or consistent service.
Market segmentation strategies often involve identifying a targeted group within an existing market. You then tailor your offerings to address their biggest pain points. Focusing on a niche group can help minimize risk by marketing to the consumers that are most likely to purchase your products or services.
Pros
- Market segmentation helps minimize risk
- Focusing on a niche market may require fewer resources
- You can scale down your operations to make your core business more efficient
Cons
- Focusing on a niche group may limit revenue and outward expansion

Business Expansion Strategy Ideas
If you are not sure which direction to take to expand your business, consider using the following expansion strategy ideas:
- Reduce your costs
- Identify your core strengths
- Perform market research
- Find new opportunities
- Develop an expansion plan
- Choose the right marketing tools
- Track progress in real-time
These ideas can help grow your business organically while allowing you to find opportunities that offer the most potential for further growth.
1. Reduce Your Costs
Start growing your business by reducing your operating costs. Limiting your costs helps increase your profit margin, allowing you to earn more revenue with each sale.
Cutting costs can make your business leaner and more efficient. You may eliminate unnecessary or costly processes, which can lead to greater productivity and less waste.
2. Identify Your Core Strengths
Exploit the strengths of your core business. Focusing on the strengths of your business instead of the weaknesses can help generate more revenue in a shorter time frame.
Studies show that strengths-based development tends to produce greater results compared to trying to improve areas of weakness. You may experience increased sales, profits, customer engagement, and other benefits simply by amplifying what already works.
3. Perform Market Research
Always perform market research when preparing to expand business operations. Whether you want to develop a new product or enter a new market, you need to research the market to analyze potential profits and risks.
Market research should include a review of competitors, market size, and demographics. You need to ensure that there is adequate demand for your products or services to make expansion worthwhile.

4. Find New Opportunities
Look for new opportunities that you may have overlooked in the past. During your market research, you may find new areas for growth. For example, the size of your local market may have grown since you first launched your business, providing an opportunity for market expansion or penetration.
You may also uncover issues that your competitors fail to address. Look for gaps in the needs of customers that can be fulfilled by your products or services.
5. Develop an Expansion Plan
After increasing the efficiency of your core business and promoting your strengths, you can start developing your expansion plan. Use the market research you completed to explore opportunities and select the best growth strategy.
Businesses that are struggling financially may benefit from diversification or a joint venture. Entering a new market can open doors to new customers. However, in most cases, it is best to start with what you already know. Focus on conquering existing markets and surpassing the competition before expanding to new regions or industries.

6. Create a Marketing Strategy
All types of expansion plans require marketing. You need to use marketing to help spread awareness of your latest efforts, whether you plan on introducing new products or entering a new market.
Businesses tend to achieve better results when combining online and offline marketing tactics. The components used for online marketing often include:
- Websites and landing pages
- Content creation (blog posts, videos, downloadable guides)
- Email marketing
- Search engine optimization (SEO)
- Paid advertising (search engines, social media ads, website ads)
90% of shoppers use the internet to search for products and services. While most people use the internet to perform research, traditional offline marketing remains beneficial to any marketing strategy.
Offline marketing can have more of an impact by leaving a lasting impression. You capture the attention of your audience with fewer distractions. Offline marketing channels are also less crowded. Common offline marketing options include:
- Pamphlet and flyer distribution
- Television and radio ads
- Newspaper and magazine ads
- Billboards and other out-of-home (OOH) advertising
Integrating online and offline marketing strategies provides a more well-rounded approach to getting the word out about a new product or service. You can target customers on multiple fronts, which helps boost awareness.
Translating web content into offline content, such as converting a blog post into an informational pamphlet, is one way to bring greater integration. You may also try adding QR codes and website URLs on flyers and other print ads. View our guide on How to Integrate Offline and Online Marketing for more tips.

7. Track Progress in Real-Time
You have a variety of tools available for tracking digital marketing campaigns. You can view website statistics, analyze SEO scores, and monitor ad campaigns.
To track your offline marketing campaigns, consider using Oppizi. You can easily plan, monitor, and track over 14 key performance indicators (KPI) related to your offline marketing strategies.
You should track the progress of all marketing efforts, sales, customer feedback, and any other area that can help you analyze the success of your expansion plans. Tracking progress helps you determine which strategies are paying off and which strategies require improvement.

How to Expand Your Business into New Markets
Entering a new market may involve diversification or expansion into a new geographical area. Each option has separate risks and rewards. Diversification involves moving into an entirely new market. This includes international markets, markets in other regions, and local markets in other industries.
For example, a local veterinary hospital may diversify its business by offering pet grooming or animal boarding. The hospital expands its reach into related industries without expanding to a new geographical area.
Instead of expanding into related industries, a veterinary hospital may choose to open new locations in other cities. This is a form of geographical expansion. The hospital retains its same practices but expands its reach.
The following steps can help you identify the best market for your expansion goals:
- Research competitor markets
- Research related product markets
- Consider your long-term business goals
- Pay attention to customer feedback
- Establish a budget for your expansion plans
- Set a timeframe for each stage of expansion
Along with these steps, you may need to review regulations and industry standards related to the market that you plan to enter. Before you sell certain products or services in other states or countries, you may need to obtain licenses or permits. You may even need to localize your products for a new audience.

1. Research Competitor Markets
One of the first steps in entering a new market is to research the competition to discover their strengths and weaknesses. Look for the areas where you are most likely to have a competitive advantage. You may find that your competitors all charge too much or lack adequate customer service. These details can help you capture a larger share of the market.
2. Research Related Product Markets
Research related products and services instead of focusing solely on existing markets. Searching related product markets can help you find new opportunities for business growth or better understand the needs of your customers.
3. Consider Your Long-Term Business Goals
Before selecting a business expansion strategy, think about your long-term business goals. Do you want to remain focused on a local market or reach international markets? Do you want to keep your operations focused on a single industry or diversify your operations into multiple industries? The answers to these questions can shape the direction of your expansion plans.
4. Pay Attention to Customer Feedback
Customer feedback can offer useful insight into the best places to direct your expansion efforts. Use customer comments from social media, review sites, and surveys. You can learn more about what they want most from the types of products or services that you offer.

5. Establish a Budget for Your Expansion Plans
Always set a budget before initiating an expansion strategy. You should take the time to estimate the costs involved. Depending on the strategy that you select, you may need to set aside funds to purchase or lease real estate, buy equipment, and hire new employees.
6. Set a Timeframe for Each Stage of Expansion
No matter your expansion plans, you need to set a schedule for each stage. For example, you may need to open a new office and hire staff within a certain timeframe or ensure that a new product is ready to launch by a specific date.
After developing your plan, setting a budget, and planning a schedule, you can initiate your strategy. Continue to track your progress using all available analytics software.

How to Expand Your Business on a Low Budget
The best way to expand a business on a low budget is to focus on internal expansion. An internal (organic) growth strategy allows you to optimize the efficiency of your current business operations to maximize revenue.
Internal growth prioritizes productivity and efficiency. If you have limited cash flow, your focus should be on making your current business practices more profitable. Find ways to remove waste and inefficient processes from your daily operations.
Try to cut costs related to your largest expenses outside of labor. This may include rent, equipment, and inventory. Downsizing to a smaller facility or office may help cut rent. Working with vendors and suppliers may allow you to save on equipment and inventory costs.
Your marketing budget may also be a large part of your monthly expenses. However, instead of cutting your marketing spending, you should find ways to increase your return on investment.
Get more out of your marketing dollars by eliminating campaigns that fail to deliver positive results and strengthening the top-performing campaigns.
Reducing spending can increase profits, which leads to moderate growth in assets. To start expanding your business, you need to acquire more customers. After improving the efficiency of your operations, choose an expansion strategy with minimal upfront costs.
Cost-effective growth strategies include market segmentation, the share of wallet (SOW) growth, market penetration, and market expansion. These strategies allow you to continue focusing on internal expansion while growing your customer base.

How to Expand a Startup Business
Outside investment is the most common path for growing a startup. A startup with an innovative product, service, or business model can seek funding to build more momentum for rapid growth.
Many startups obtain their initial capital from angel investors and investment firms. This is often referred to as “seed” funding, as it allows the startup to launch its operations. When a startup needs additional funds, it may initiate Series A funding.
According to Investopedia, the average Series A funding was $10 million. Startups that receive Series A funding typically have a growing user base and consistent revenue. Series A funding is often followed by Series B and Series C funding, allowing startups to continue taking their businesses to the next level.
Yet, when a startup struggles to maintain consistent revenue or establish a customer base, it will likely struggle to obtain funding. If your startup is facing declining revenue, use the previous suggestions for business expansion on a limited budget. Focus on improving the efficiency of your operations to turn a profit before expanding.
Startups that cannot build a customer base may also need to go back to the basics. Use a market segmentation strategy to consolidate your efforts to a smaller portion of the market. Downsize your operations while focusing on a niche market to become more profitable.
Reducing your business expenses by 10% can give you more funds for marketing, which you can use to reach your niche audience.
Startups may also increase their chances of success by relocating to a different geographical area. Switching to a different city, state, or country may offer more potential.
For example, you may face limited growth opportunities in your current location. Moving to a bigger city or covering a larger region offers access to more customers. Instead of more customers, moving to another location may offer access to lower costs, such as cheaper rent or lower wages.
How to Develop Your Business Expansion Strategy
The strategies that you choose will likely depend on your budget, current growth rate, and the size of your current markets. Entering new markets tends to require more funds and resources compared to digging deeper into existing markets.
Businesses with limited budgets may benefit from focusing on internal growth. Increasing efficiency and productivity can make a business more profitable, which leads to more opportunities.
Startups often rely on funding to help fuel expansion efforts. Bringing in outside investors can help you go to market faster and provide access to more distribution channels.
For additional advice on developing an effective strategy, check out our Ultimate Guide for Business Expansion.
Conclusion
Business expansion is necessary for sustainability. In most industries, you need to continue acquiring customers or get existing customers to spend more to achieve consistent growth.
Most business growth strategies are internal/organic or external/nonorganic. Organic expansion involves actions that you take internally, such as improving productivity or developing new products. You may also try expanding into new markets or increasing penetration in an existing market.
Inorganic expansion includes strategies that rely on external resources, such as other businesses. Examples include mergers and joint ventures.
No matter the path you choose, you need to develop a thorough expansion plan with clear strategies and goals. Remember to use a combination of online and offline marketing to promote your efforts and track your offline KPIs.